Droplet Evaporation Condensation Frosting
Droplet Evaporation
The MTEL has investigated the droplet evaporation characteristics from a mechanical engineering point of view by looking at the evaporation dynamics through experimental/numerical methods.
The droplet evaporation on the anodized surfaces
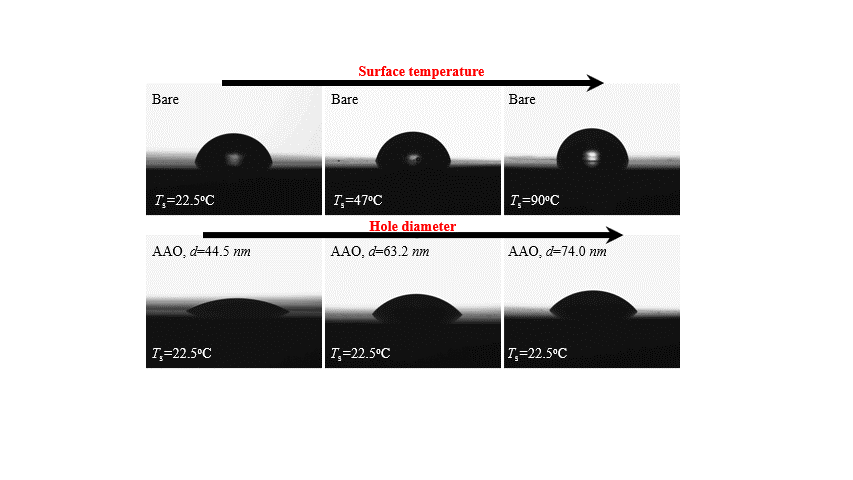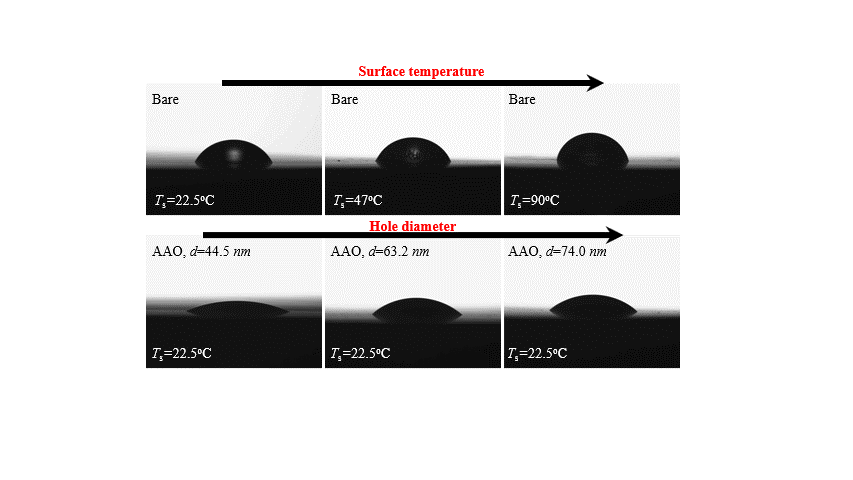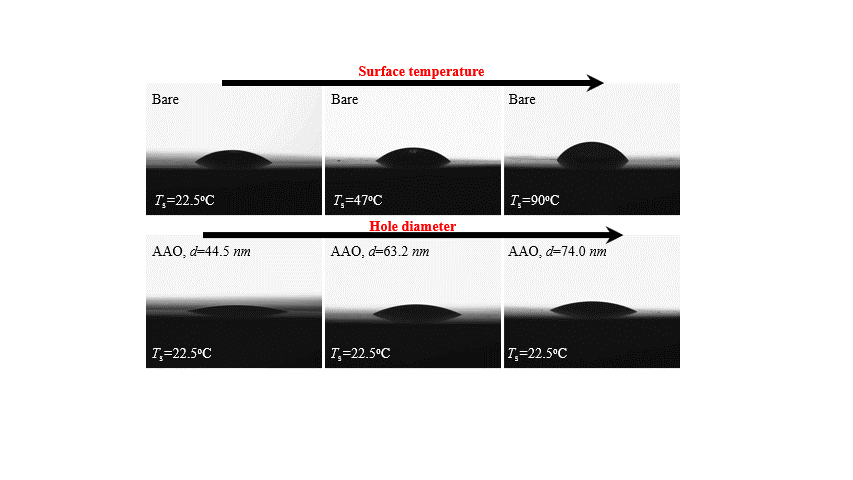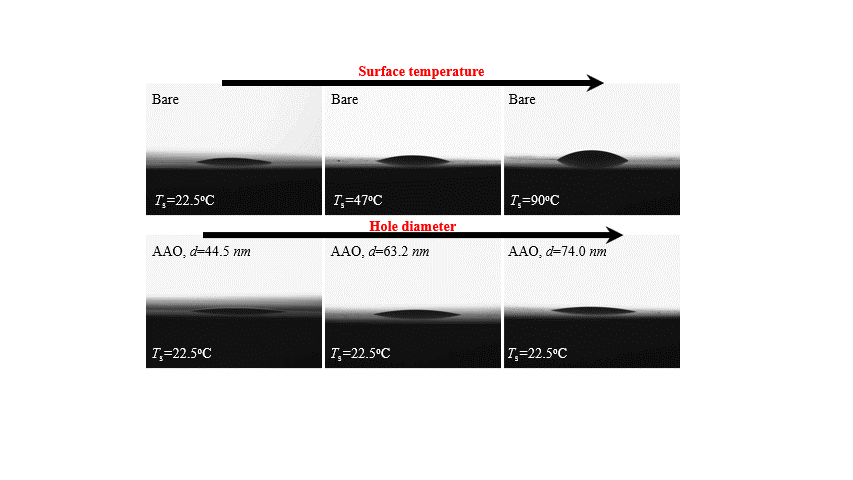
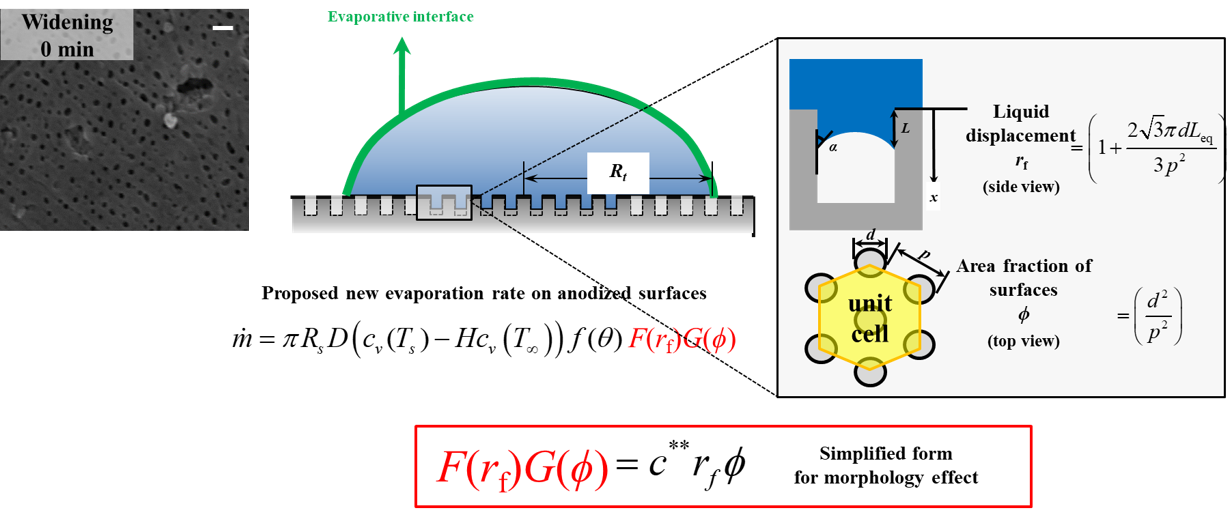
We have investigated the sessile droplet evaporation and mass transfer characteristics on the anodized hole-patterned surfaces and proposes a theoretical model based on the experimental data. Polished aluminum specimens and oxalic acid are utilized to generate anodized surfaces with three cases by changing area fractionsand hole diameter. The anodized hole surface contributes to enhancing surface wettability with higher capillaryforce inside the holes on the surface. The droplet evaporation rate increases with a reduction in the hole dia-meter. It is found that the previous models of the evaporation heat transfer rate on the bare surface do notfit wellwith the experimental results for the anodic oxidation surface. The solid-liquid-air interfacial equations involving the Gibbs energy are newly established for development of a new evaporation model that considers of the liquid displacement length.
Related published articles are as follows:
•Joo Hyun Moon, Sang Min Lee, Chang Kyoung Choi, Seong Hyuk Lee, Modeling of the evaporation rate of liquid droplets on anodized heated surfaces, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol. 98, pp.209-215. (IJ100, IF=4.463)
•Joo Hyun Moon, Chang Kyoung Choi, and Seong Hyuk Lee, Local evaporation flux of evaporating droplet on heated aluminum surfaces, Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, under review
The selective evaporation of binary mixture droplet (BMD)
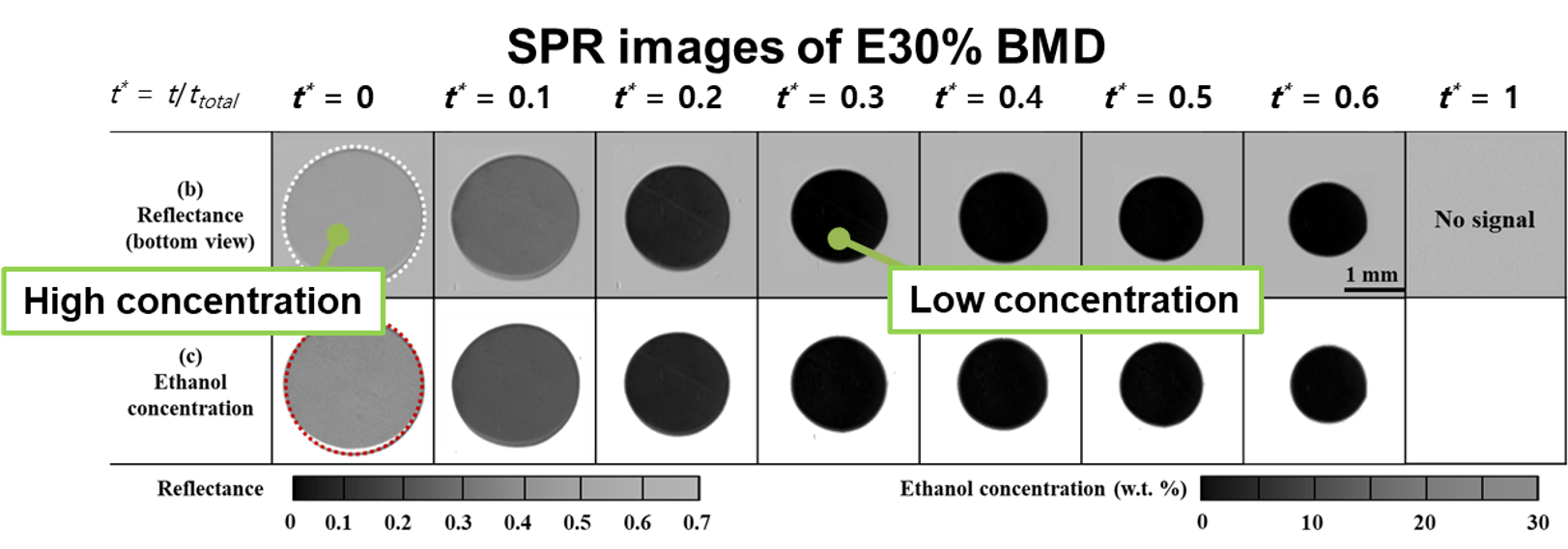
A challenging task to measure the temporal concentration change of Binary Mixture Droplet (BMD) was performed by MTEL with the collaboration of Prof. Choi at Michigan Technology University. We successfully carried out the in-situ measurement of ethanol concentration change of evaporating BMD by using the Surface Plasmon Resonance imaging (SPRi) and proposed the prediction model of selective evaporation of ethanol-water BMD.

Related published articles are as follows:
- Chan Ho Jeong, Hyung Ju Lee, Dae Yun Kim, Shahab Bayani-Ahangar, Chang Kyoung Choi, and Seong Hyuk Lee, Quantitative analysis of contact line behavior of evaporating binary mixture droplet using surface plasmon resonance imaging, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol. 165. February, 2021.
- Chan Ho Jeong, Hyung Ju Lee, Chang Kyoung Choi, and Seong Hyuk Lee, Selective evaporation rate modeling of volatile binary mixture droplets, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, under review
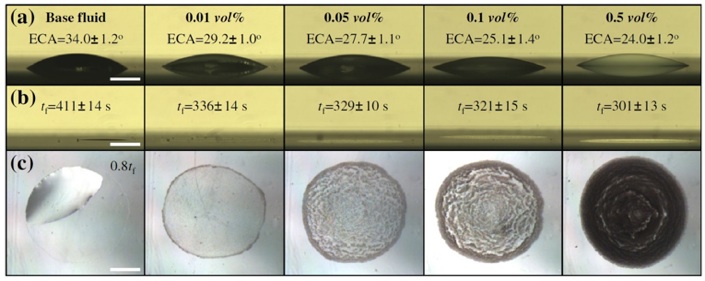
Local Aggregation of Nanoparticles (Macroscopic view)
We experimentally investigated non-uniform particle distributions and evaporation characteristics of a nanofluid droplet on a hydrophilic surface. Using an inverted microscope, the size distribution of aggregated nanoparticles was visualized and analyzed at the different sight of view locations. From the digital images captured using CMOS cameras and a magnifying lens, the effect of particle concentrations on droplet evaporation rates was examined. Local aggregation was observed when a nanofluid droplet was in contact on the surface, suggesting that the non-homogeneous characteristics should be considered in estimating thermal conductivity of a nanofluid droplet.