Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Free piston stirling cooler (FPSC)
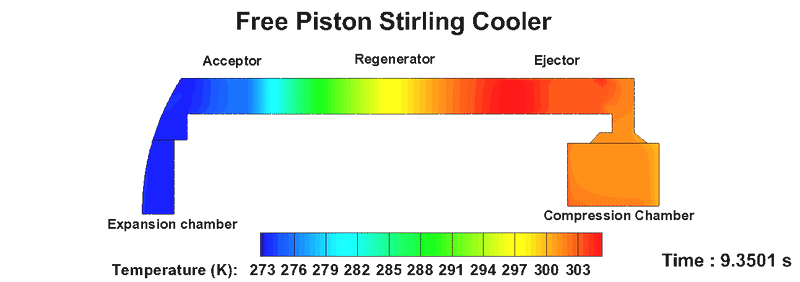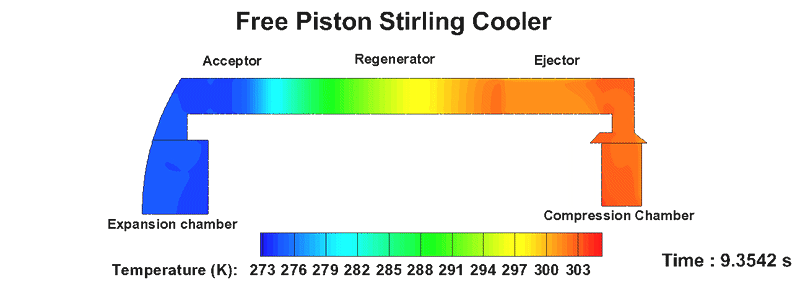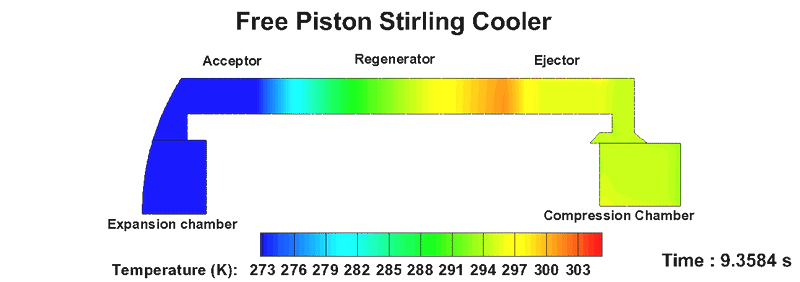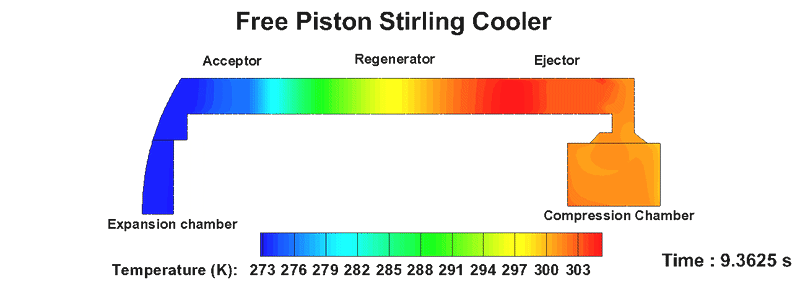
- Stirling Cooler is a cooling device that uses an eco-friendly working fluid and is a fully enclosed heat transfer system.
- It is used in small refrigerators, military industry, space industry, superconductor, and carbon dioxide capture.
Ceramic heater for electrostatic chuck
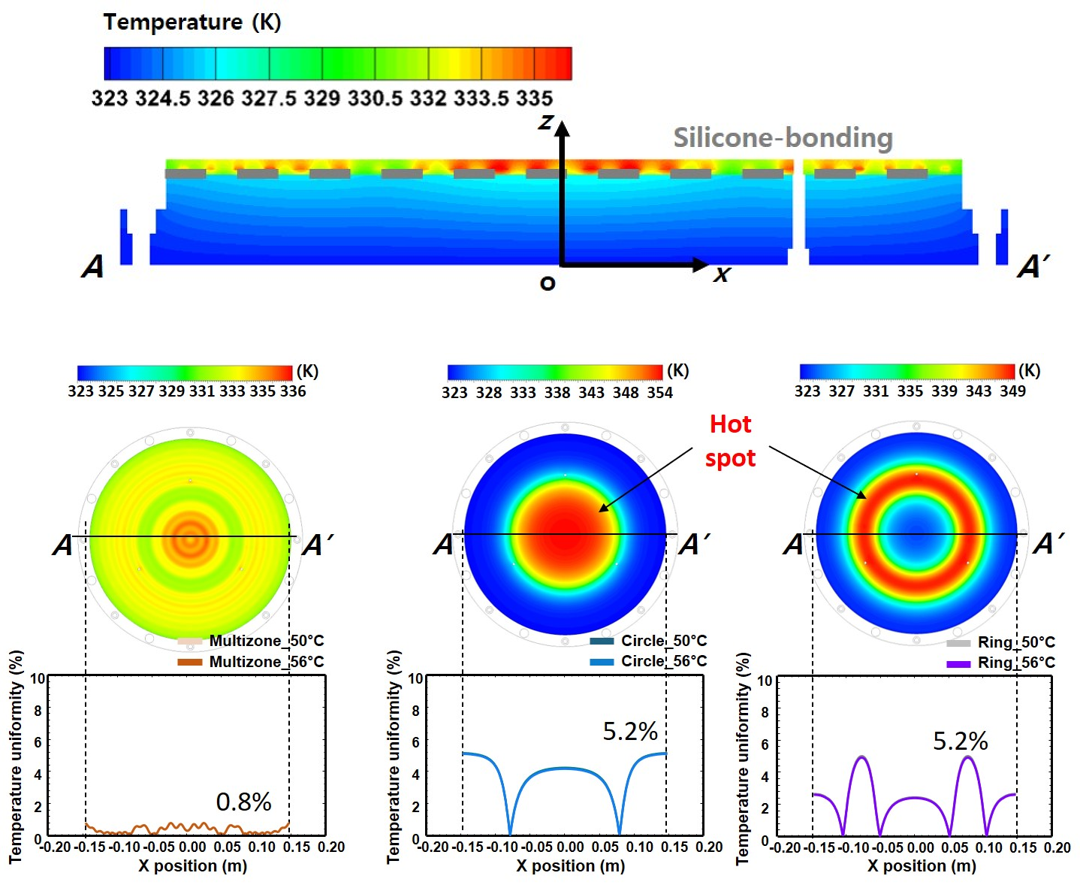
- Electrostatic chuck is used to fix and transfer the wafer in the semiconductor process.
- Temperature uniformity is an important parameter in electrostatic chuck to produce high-quality semiconductor.
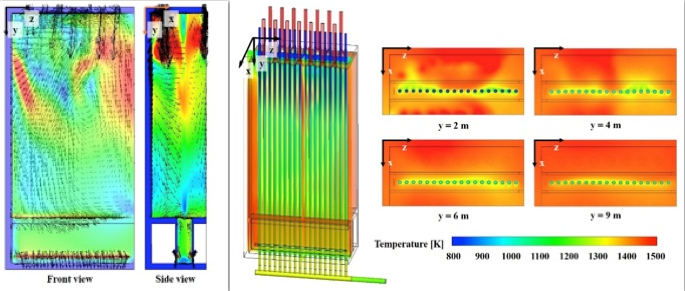
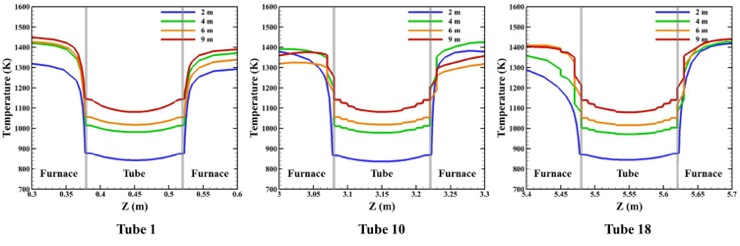
Heat transfer characteristics and thermal deformation in a steam reformer refinery
The consumption of petroleum oil increased 7 folds over the past 50 years due to increase in population and industrial development. Therefore, various types of alternative fuel are being developed with the developed countries in the forefront. However, cracks and bending could occur in tubes because the reforming reaction of hydrogen occurs at a very high temperature. Aging problems of equipment and parts from prolonged operation occur in the related industries. Therefore, technical issue receiving attention in recent years is an effective operating method through plant safety and estimation of replacement period for parts, and the study in this area is required.
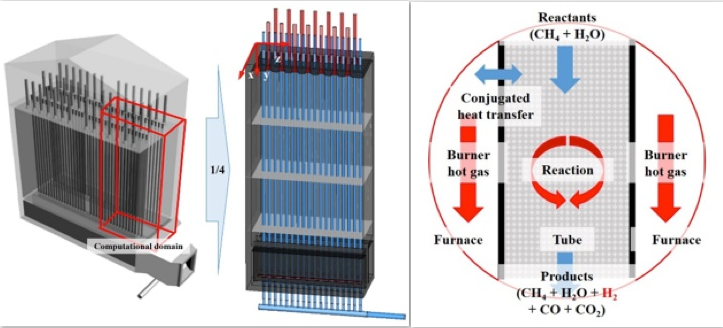
Therefore, this study performed a numerical simulation to examine the conjugate heat transfers characteristics and the thermal deformation in the 3-D geometry steam reformer refinery. As one of method for reducing thermal deformation, the fixed supports which can be mounted locally at the tubes are being used in many industries. Thus, the present study numerically reports the influence of tube supports on variation of thermal deformation.
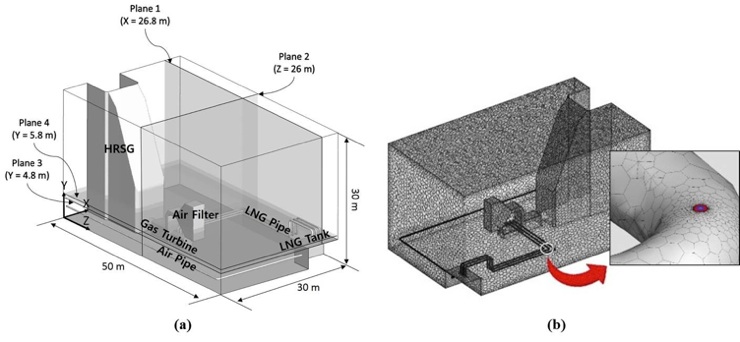
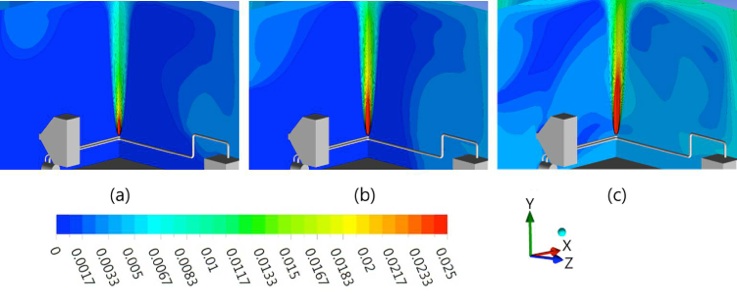
Effect of crack size on gas leakage characteristics in a con fined space
The demand for Combined cycle power plant (CCPP) has been continually increasing in advantages on economic and environmental sides. In addition, CCPP is preferred in utilities for peak generation at industrial facilities or on site power generation due to the capability of a wide range of configurations and capacities. In South Korea, the CCPP fueled by natural gas is actually supposed to be constructed in underground. Natural gas has been referred to as a low-carbon fuel as its combustion produces significantly less carbon dioxide (CO2) than from gasoline, diesel, or coal combustion on an energy-equivalent basis. However, natural gas is mainly composed of methane gas, which is colorless and odorless. The gas leaked from a high-pressure pipe line rapidly spreads around. Therefore, it is necessary to understand gas leakage characteristics in the under-ground CCPP prior to formulating counterplans for preventing accidents.
Thus, this study conducted numerical simulations for a confined space, simplifying the combined cycle power plant to investigate the crack size effect on gas leakage characteristics. The gas leakage model in a pipeline was suggested to predict the mass flow rate from the leak according to the crack size. Also, the parameters related to LFL of the methane, e.g., the risk region and leakage distance, were quantitatively analyzed to compare the potential risk due to a gas leak.